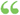 ... the product of the two, plus the square of the second. In the third case, we have (a + b) (a — 6) = a2 — b2. (3) That is, the product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares. ... the product of the two, plus the square of the second. In the third case, we have (a + b) (a — 6) = a2 — b2. (3) That is, the product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares.  A Treatise on Algebra - Pàgina 189per Elias Loomis - 1846 - 346 pàginesVisualització completa A Treatise on Algebra - Pàgina 189per Elias Loomis - 1846 - 346 pàginesVisualització completa - Sobre aquest llibre
 | Horatio Nelson Robinson - 1850 - 256 pàgines
...power of a quantity, it always means the power of its numeral value considered abstractly. (ART. 17.) THE PRODUCT OF THE SUM AND DIFFERENCE OF TWO QUANTITIES IS EQUAL TO THE DIFFERENCE OF THEIR SQUARES, as will be seen by inspecting the following products : The first example should be multiplied in full... | |
 | William Smyth - 1851 - 272 pàgines
...a be one of the quantities and b the other ; then (a + b) (a — b) = a? — b2. We thus learn that the product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squareS. These propositions are demonstrated, in geometry, in another form, where it is shown, 1°, That if... | |
 | Joseph Ray - 1848 - 250 pàgines
...^ But a+6 represents the sum of two quantities, and a — b, their difference ; hence, THEOREM III. The product of the sum and difference of two quantities, is equal to the difference of their squares. EXAMPLES. 1. (5+3)(5-3)=25-9=16=8X2. 2. (2a+6)(2a— 6)=4a*— V. 3. (2z+3y)(2x-3y)=4z'-9i/2. 4. (5a+46)(5a—... | |
 | Joseph Ray - 1852 - 408 pàgines
...j02=4z2— 4ijr+y2. 3. (3x—5zy=9xi— 30xz+25z2. 4. (02— 3cx)2=o2z2— 6 ART. 8O. THEOREM III. — The product of the sum and difference of two quantities, is equal to the difference of tlieir squares. Let a represent one of the quantities, and 6 the other ; then o-|-i=their sum, and... | |
 | James William M'Gauley - 1854 - 284 pàgines
...+6 By a— b -ab—b2 Product a2— 62 The following formula is obtained from this example : — " the product of the sum and difference of two quantities, is equal to the difference of their squares." And, for the reason just given [35] it, also, is general. 37. EXAMPLE 3. — Multiply c — d By c... | |
 | Elias Loomis - 1855 - 356 pàgines
...5— x/3 Product, 25-3=22, as required. These two examples are comprehended under the Rule in Art. 62, the product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares. Ex. 3. Find a multiplier that shall make v/5+v/3 rational and determine the product. Ex. 4. Find a... | |
 | Charles Davies, William Guy Peck - 1855 - 628 pàgines
...number of factors. The following are some of the properties of products with respect to their forms : 1. The product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares ; that is, (x + y) (x — y) = x' — y'. 2. Twice the sum of two squares is equal to the sum of two... | |
 | William Smyth - 1855 - 370 pàgines
...quantity, minus the double product of the first by the second, plus the second power of the second. 5. The product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their second powers. The questions, art. 15, will furnish additional exercises for the learner in stating... | |
 | Elias Loomis - 1856 - 280 pàgines
...beginners often commit the mistake of putting the square of a— b equal to af—h\ THEOREM III. (67.) The product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares. Thus, if we multiply a +b by a —b a'+ab -ab-b' we obtain the product a'- b'. Examples. Ex. 1. (3a+^b)(3a-4b)=9a'-16b\... | |
 | Harvey Goodwin - 1857 - 692 pàgines
...following manner. It is easily seen by actual multiplication, that (a + 6) x (a - 6) = a- - b\ or that the product of the sum and difference of two quantities is equal to the difference of their squares; a theorem which may be used in the multiplication of such quantities as those in the last example,... | |
| |